Bacterial Diseases (continued)
| Meningococcal Infection | Types A, B, C |
| Severe disease:
|
Transmitted by droplets via upper respiratory tract Mainly children < 10 yrs. old Acute meningococcal septicemia & meningitis |
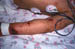
| Rash:
|
40-90% of cases Pink macules - purpura nearly any site |
| Severe cases: | Extensive ecchymoses or necrotic ulcers; associated with high mortality |
| Diagnosis: | Blood/CSF culture |
| Corynebacterium minutissimum: | Causative agent of erythrasma |
| Erythrasma: | Sharply marginated erythematous patches with fine scale of axillae and groin |
| Diagnosis: | Wood's light exam (reveals coral red fluorescence) |
| Pigment formation: | Blue-green pyocyanin; greenish-yellow fluorescein Colonizes burns, ulcers, moist skin lesions, and nails |
| Infancy: | Periumbilical |
| Burns: | Leading to secondary septicemia |
| Hot tub folliculitis: | Worse in areas covered by bathing suit Settles spontaneously 7-10 days Hot tubs/whirlpool; chlorination no help |
| "Tropical immersion foot": | Toe webs, maceration Sharply demarcated maceration tinged with green |
| Pseudomonas septicemia: | Severely compromised host Bullae (moist areas: axillae/perineum/buttocks) -> necrotic ulcers: ecthyma gangrenosum Prognosis grave even with early treatment |
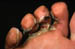
Borrelia burgdorferi |
|
| Tick bites: | Ixodes dammini/pacificus |
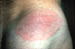
| Lyme Disease:
|
Skin disease plus a disease of nervous system, heart and joints |
| Erythema chronicum migrans (ECM):
|
1-36 days after bite. Untreated lesion fades within a
few weeks. Dissemination of infection is from days to weeks after inoculation. Arthritis/neural (meningitis, cranial nerve palsies), myocarditis, conduction defects. |
| Other cutaneous manifestations: | °2 lesions of ECM in 10% of patients. Lesions are
smaller and less migratory. Lymphocytoma Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans ?Morphea/LSA |
| Diagnosis: | Serology, tissue culture |
Treponema pallidum |
Increasing incidence |
| Incubation: | 9-90 days |
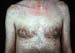
| Cutaneous manifestations: | |
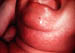
| °1 lesion: | "Chancre" - painless ulcer with indurated edge |
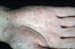
| °2 lesions: | Macules, papules of trunk, palms, and soles; condylomata; hair loss |
| °3 lesions: | Gumma (full thickness tissue destruction) |
| Congenital syphilis: | "Snuffles" Stigmata of congenital syphilis (Hutchinson's teeth, sabre shins) |
| Rapid course in HIV+ patients: | May have negative serology & may not respond to conventional treatment |
| In HIV: | Primary chancre may be painful secondary to Staph. super-infection |
| Diagnosis: | Dark field examination, serology (VDRL, RPR, FTA-ABS, ELISA) |